Treatment Strategies
Total Colonic Aganglionosis: When and How To Do the Pull-through
Presentation Summary
Obstetric and Gynecologic Considerations in Patients with Anorectal Malformation
Presentation Summary
Management of Anorectal Malformations in Male Patients
Presentation Summary
6-Year-Old Female Patient Presents with Right Lateral Leg Staining
- 6yo F who presented in first year of life with right lateral leg staining
- Imaging at 2 yr of age demonstrated marginal vein
Treatment Options
- Patient progressed to syncopal episodes while wearing compression, likely due to large size of marginal vein
35-Year-Old Female Patient Presents with Purple Stain to Right Lateral Thigh
- 35yo F presents to CHCO VAC 11/2018
- Purple stain to right lateral thigh, RLE overgrowth, blebbing to foot, right buttock, groin
- Evaluated at multiple facilities throughout lifetime and received multiple diagnoses
- Has undergone several surgical excisions of bothersome “hemangiomas”
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis in Children: Discussion and Q&A Video
mmmmm
3-Year-Old Female Patient Admitted to ER with Fever and Vomiting
Case Summary
- 3-year-old female patient, born and raised in São Paulo, Brazil
- Previously healthy
- Admitted to E.R. with a 2-d history of fever and vomiting
- Right Otitis Media diagnosed in another service, treated with azithromycin.
- Developed with worsening of symptoms and bilateral convergent strabismus, more accentuated to the right
14-Year-Old Male Patient Admitted with Left Visual Loss and Altered Level of Consciousness
Case Summary
- 14-year-old, male, born and raised in São Paulo, Brazil.
- Previously healthy.
- Admitted to E.R. with left vision loss and altered level of consciousness.
- Recurrent episodes of headaches during the past 30 days, blurred vision, and poor balance.
Five-Day-Old Female Patient Referred with Esophageal Atresia (Hendren Patient Case)
- 5-d-old baby girl referred July 1963 with esophageal atresia.
- X-ray study had shown a blindly ending upper esophagus; abdominal film showed no gas in the abdomen.
- Stamm gastrostomy using a mushroom catheter was performed, bringing the tube out through a small stab wound.
- Right chest was opened to confirm for certain that the distal esophagus was rudimentary (having seen a prior case where a small fistula had been present, with a good lower esophagus but without abdominal gas). (Modern imaging would obviate that need.)
- Upper pouch was mobilized, during which a fistula was seen from the back of the upper pouch to the trachea, not seen on pre-op study.
- Fistula was divided and closed.
- After chest closure, infant was turned and a transverse incision in the lower neck just above the clavicle anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the jugular vein and carotid artery.
- Previously freed upper esophagus was quickly opened and sewn to the wound to provide free drainage of saliva.
- Baby thrived.
Fig. 1. Patient at Age 10 Mo Before Colon Esophagus Operation. Note excellent nutritional status. Upper esophagus stoma to drain saliva above left clavicle. Gastrostomy tube covered with ample tape to avoid its being pulled out.
- At 10 mo, through a left 7th interspace thoracoabdominal incision, a colon esophagus was made using transverse colon on a left colic arterial pedicle (see video of operation).
- Lower end of colon esophagus did not lie comfortably for anastomosis to the distal esophageal remnant and so it was anastomosed to the anterior wall of the stomach.
- Postoperatively, when gastrostomy feedings were begun barium study showed free reflux up the colon conduit and less flow through the pylorus, although both vagi were spared intraoperatively.
- At 2 weeks postop, laparotomy was performed.
- Gastrostomy tube site was moved farther proximally in the upper stomach.
- Generous Heineke-Mikulicz pyloroplasty was performed, incising 1 inch (2.54 cm) into the duodenum and 1.5 inches (3.81 cm) into the stomach, closing transversely. Pyloric tissues were indeed thicker than expected.
- Colon esophagus remained somewhat dilated as if there were functional partial obstruction at its lower end.
- Some gastrointestinal blood was observed on multiple occasions, never great in amount.
- At 10 wk, reoperation was performed to accomplish three tasks:
- (1) shorten the lower end of the colon esophagus;
- (2) anastomose it to the original rudimentary lower esophagus, as once considered; and
- (3) divide both vagus nerves to reduce gastric acidity.
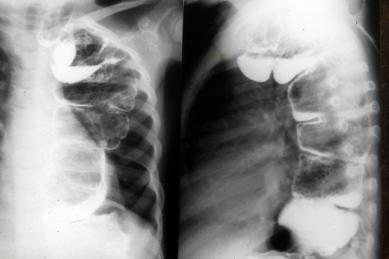
Fig. 2. Barium Swallow in 1968. Although caliber of colon was still somewhat dilated it emptied well, there was no aspiration, and patient was well nourished.
- Patient thrived; family moved to Oklahoma.
- At age 3 yr, she was seen. She and her barium study were both fine.
- At age 22 yr, patient was and healthy.
- Unable to get pregnant, she underwent laparoscopy elsewhere; after lysis of fallopian tube adhesions she had two healthy sons.